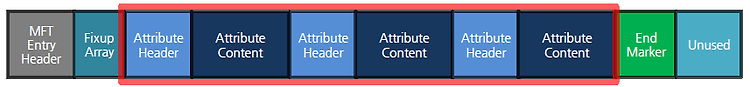
MFT - Attribute
속성 종류
MFT Entry Header, Fixup Array에 이어 이번에는 Attributes에 대하여 알아보자. Attributes는 각 파일의 메타정보를 표현하고 있으며 Attribute Header + Attribute Content로 구성되어 있다. 크기에 따라 Resident와 Non-Resident 속성으로 구분하며 총 17가지의 속성이 있다. 이러한 속성은 각 각 다른 Header를 가지며 기본적으로는 $STANDARD_INFORMATION, $FILE_NAME, $DATA를 가진다. 아래의 그림과 같다.
이러한 속성은 Fixup 배열 이후 End Marker가 올 때까지 연속적으로 오며 각 속성은 위에서 말한 바와 같이 속성헤더와 속성 내용으로 나뉘어진다. 우선 속성 헤더와 속성내용에 대하여 알아보기 전에 속성의 종류에 대하여 먼저 알아보자.
일반적인 파일의 경우 위에서 말한 바와 같이 $STANDARD_INFORMATION, $FILE_NAME, $DATA를 가진다고 이야기 하였다. 따라서 3가지 속성에 대해서만 잘 알고 있어도 대부분의 파일을 분석할 수 있다. 아래의 그림을 보자.
현재 내 PC의 MFT를 나타낸 것이다. MFT Entry Header에서 속성이 시작되는 위치는 0x38이라 나타나있다. 해당 부분을 보면 속성 식별 값이 0x10으로 이는 $STANDARD_INFORMATION을 나타내고 있으며 뒤로 가다 보면 0x30으로 $FILE_NAME 속성 식별 값이 존재하는 것을 볼 수가 있다. 이러한 식별 값을 통해 어떤 속성인지 확인할 수가 있다.
Resident 속성과 Non-resident 속성
이제 크기에 따른 분류로 Resident 속성과 Non-resident 속성이 있다하였는데 이에 대하여 조금 더 알아보자. Resident 속성은 속성의 내용이 Attribute Header (속성 헤더) 바로 뒤에 위치하는 속성이다. 이에 반해 Non-resident 속성은 Attribute Content(속성 내용)이 너무 크기 때문에 MFT엔트리(1024Byte) 내부에 넣지 못할 경우, 별도의 클러스터를 할당 받아 저장(클러스터 런으로 관리)하는 방식이다. 이때, 속성 내용 위치에는 할당 받은 클러스터의 위치 정보가 저장되어 있다.
대부분의 속성은 모두 Resident 속성이고, $DATA, $ATTRIBUTE_LIST와 같은 속성은 Size가 크기 때문에 Non-resident가 될 수 있다. $DATA는 파일의 내용을 표현하는 속성인데, 파일의 내용이 MFT 엔트리 내에 저장되지 못한다면 Non-resident 속성이 된다. 대부분의 파일 크기가 크므로, 일반적으로 700바이트 이하가 아니라면 대부분 $DATA 속성은 Non-resident 로 존재한다.
위 그림은 3번째 속성이 Non-resident 인 것으로, 1,2번 속성과는 다르게 속성내용(Attribute Content)의 위치에 Cluster가 위치해 있다. 이러한 클러스터는 해당 속성 내용을 담고있는 부분을 별도의 곳에 놓아둔 것이다.
같은 파일 2.txt이지만 690 바이트일때는 디스크에서 크기를 차지하지 않았지만 698 바이트가 된 뒤에는 1 Cluster 만큼의 크기를 차지하는 것을 확인할 수가 있다. 이는 기존의 2.txt는 $DATA에 모두 담을 수 있었지만, 크기가 커지며 별도의 클러스터를 할당하므로 이러한 데이터를 관리하려고 했기 때문에 하나의 클러스터가 할당된 것이다.
다시 돌아와 속성에는 속성헤더와 속성내용이 있다하였다. 이제 이 중에서 속성헤더의 구조를 한번 살펴보자. 속성은 위에서 말한 바와 같이 크기에 따라 구분되는데 이 경우 구조가 서로 다르다는 점이다. 우선 Resident와 Non-resident 모두에 쓰이는 공통적인 속성 헤더를 살펴보자.
Attribute Header Format
공통적으로 포함되는 구조는 아래의 그림과 같다. type ID와 속성의 길이를 나타내는 등의 정보가 있다.
Attribute type ID는 속성 타입 식별 값으로 위에서 0x10이 $STANDARD_INFORMATION이였던것과 같은 값을 나타낸다. Length of attr은 속성 헤더를 포함한 속성 전체의 길이를 나타내며 Nreg Flag(Non-resident flag)는 해당 속성이 Non-resident 속성인지의 여부를 나타내며 0일 경우 Resident이며 1일 경우 Non-resident임을 알 수 있다. LenNam(Length of name)은 해당 속성 이름의 길이를 나타내고 이러한 속성 이름이 저장된 곳의 시작 위치를 Offset to name이 가지고 있다. 속성헤더 내에 있는 Flags는 속성의 상태를 표현하는데 0x0001은 압축된 속성, 0x4000은 암호화된 속성, 마지막 0x8000은 Sparse 속성을 나타낸다. 마지막 값인 Attr ID는 속성의 고유한 식별자로 MFT Entry에 같은 속성이 여러 개일 경우 구별하기 위해 사용한다.
위의 그림과 같이 MFT 엔트리 헤더에서 Offset to First attribute 값을 통해 0x38로 온 후다. 이를 해석해보면 우선 속성 식별 값이 0x10으로 이는 $STANDARD_INFORMATION 임을 알 수가 있다. 속성 헤더를 포함한 속성 전체의 길이는 0x60으로 0x98에선 다음 속성의 식별 값이 나와야 한다. 해당 속성은 현재 Resident이며 속성 이름이 존재하지 않기에 해당 위치 0x38 + 0x18 인 0x50부터 바로 속성 내용이 시작된다. 상태플래그는 0이며 속성 식별자 또한 0이다.
Resident Attr Header
Resident(거주) 속성의 헤더는 위의 공통된 속성 헤더 뒤에 다음과 같은 구조를 가지고 있다. 아래의 그림을 보자.
Size of Content는 헤더 뒤에 오는 속성 내용의 크기를 나타내며 Offset to content는 속성 내용이 시작하는 곳의 위치를 나타낸다. idx flag(Indexed flag)는 값을 "1"로 가질 경우 인덱스된 속성임을 뜻하며 $FILE_NAME의 경우 "1"로 설정되어있다. 마지막 Attr Name은 속성 이름이 있는 경우 속성 이름을 나타내고 없는 경우엔 바로 속성 내용이 온다.
공통된 헤더를 제외하고 0x48부터 resident attr header가 위치한 것을 볼 수 있다. 우선 속성 내용의 크기는 0x48이며 속성 내용의 시작 위치는 0x18로 공통 속성헤더를 기준으로 0x18뒤에 속성 내용이 시작된다는 것으로 보라색 박스와 같이 표시하였다. Index 플래그는 설정되어 있지 않으며 마지막 한 바이트는 사용되지 않는 값이다.
Non-resident Attr Header
Non-resident(비거주) 속성의 헤더 역시 공통된 속성 헤더를 지닌다. 그 뒤의 구조는 다음과 같으며 이에 대해선 표로 설명하겠다.
Non-resident는 속성 내용이 외부 클러스터에 저장되어 있으므로 해당 클러스터 정보를 담고 있는 런리스트의 정보가 필요하다. 여기서 VCN은 특정 파일의 첫 번째 클러스터부터 순차적으로 부여한 번호로 $DATA 속성의 경우 데이터가 매우 많이 조각나 있을 경우 클러스터 런의 정보를 저장하기 위해 하나 이상의 MFT 엔트리를 사용하게 된다. 이때, 런리스트의 시작과 끝을 표현하기 위해 VCN을 쓴다.
* LCN : 볼륨의 첫 번째 클러스터부터 순차적인 번호 / VCN : 파일의 첫 번째 클러스터부터 순차적인 번호
우선 런리스트 시작VCN이 0임을 알 수가 있고, 끝 VCN이 0x02803F임을 알 수가 있다. 이러한 런리스트의 시작 위치는 0x0040이며 압축 속성이 아니기 때문에 압축 단위 크기는 0이된다. 속성 내용 할당 크기(클러스터크기)는 0x28040000(671350784)이며 속성 내용 실제 크기도 0x28040000(671350784), 그리고 속성 내용의 초기화된 크기도 0x28040000(671350784)인 것을 확인할 수가 있다. 이 경우 속성의 이름이 존재하지 않는 것 또한 같이 확인할 수가 있다.
런리스트 끝VCN이 0x02803F이라는 것은 현재 $MFT 속성 내용을 표현하기 위해 0x02803F + 1개의 클러스터를 사용하고 있다는 것이다. 0x028040에 클러스터 크기 4096을 곱해주면 0x28040000으로 이는 속성 내용 할당 크기와 일치하는 것을 알 수가 있다.
* 꼭 기억해야할 점은 속성 이름의 경우, 속성 이름이 존재하는 경우에만 해당 헤더 영역이 할당된다는 점이다. 속성 이름이 없는 경우 해당 영역을 제외하고 바로 속성 내용이 뒤따라 온다.
Cluster Runs (클러스터 런)
속성이 Non-resident인 경우 별도의 클러스터를 할당 받아 내용을 저장한다고 했다. 할당 받는 클러스터가 내용의 크기에 따라 하나에서부터 수천개까지 될 수 있다. 이 클러스터들은 연속적으로 할당 될 수 있지만, 대부분 비연속적으로 할당된다. 이렇게 비연속적으로 할당된 클러스터들을 효과적으로 관리하기 위한 것이 클러스터 런이다. 다음은 클러스터 런을 표현하는 런리스트(Runlist)의 예를 그림으로 나타낸 것이다.
첫 바이트를 읽어 2개의 용도로 사용하는 것이다. 가령 첫 바이트가 '0x32'인 경우 런 길이는 2바이트를 읽어야하며, 런 오프셋은 3바이트를 읽어야 한다는 것이다. 말로만 해서는 어려우니 아래의 그림을 참고하자.
첫 번째 클러스터 런의 첫바이트가 '33' 이므로, 오프셋 3바이트와 길이 3바이트를 읽어야 한다. 먼저 길이의 경우 바로 2번째 바이트부터 나오며 첫번째 바이트에서 뒷자리가 3이므로 총 3바이트 읽어 0x00C820이 된다. 오프셋은 첫바이트의 앞자리가 3이므로 3바이트를 읽어 0xC00000이 된다. 이는 Offset 0x0C0000번 클러스터부터 0xC820(51232)개의 클러스터가 할당되어 있음을 나타낸다.
두 번째 클러스터 런은 첫바이트가 똑같이 33이므로 위와 같으며 이는 오프셋 0x57E23D 클러스터부터 0xEA1B(59931)개의 클러스터가 할당되어 있음을 나타낸다.
세 번째 클러스터 런은 첫바이트가 '42'이다. 클러스터의 길이는 첫바이트의 뒷자리가 2이므로 2바이트를 읽어 0x0308이 되며 오프셋은 앞자리가 4이므로 4바이트를 읽어 0x0124727B가 된다. 이는 0x0124727B 클러스터에서부터 0x308(776)개의 클러스터가 할당되어있음을 알 수가 있다.
* 수정 : 첫 번째 클러스터위치인 C0000클러스터는 해당 오프셋 0xC0000000이 맞지만, 두 번째 클러스터 런인 57E23D는 0x57E23D000이 아닌 여기에 앞의 클러스터 값을 더해주어야 한다. 따라서 +0xC0000000을 해야한다. 세 번째부터는 마찬가지로 앞의 두개를 더해주어야한다.
이렇게 총 5개의 클러스터 런이 형성되어 있는 것을 확인할 수가 있으며 각 클러스터 런의 길이를 모두 더해보자. 그러면 0x28040이 나오며 10진수로는 163,904개의 클러스터가 형성되어있다는 것이다. 여기서 하나의 클러스터는 크기가 4KB이므로 4를 곱해주면 655616이 된다. 이를 이제 1024로 나누어주면 640MB가 되며 이는 현재 $MFT 파일의 크기와 같음을 알 수가 있다.
이렇게 대부분의 파일은 $DATA의 값이 크기 때문에 Non-resident이며, 이는 클러스터 런을 가지므로 각 각 떨어져 있는 클러스터들의 위치를 알 수가 있었다. 이해가 잘 안된다면 바로 위의 예제처럼 직접 파일의 크기와 함께 맞추어 보는 것도 하나의 좋은 방법인 것 같다.
또한 클러스터 런을 활용하면 $MFT 파일을 쉽게 수집할 수가 있다. $MFT는 NTFS에 존재하는 모든 파일의 메타 정보를 가지고 있기 때문에 메타 정보만을 가지고 포렌식 분석을 수행하고자 할 경우, $MFT 파일을 수집하는 것이 필요하다. $MFT 파일의 MFT 엔트리도 $MFT에 있으므로, $MFT에서 $MFT 파일의 MFT 엔트리를 찾은 후, 해당 엔트리의 데이터 속성의 런리스트를 확인한다. 그리고 런리스트의 정보대로 데이터를 읽어서 연결하면 하나의 $MFT 파일이 된다.
출처 및 참고
http://forensic-proof.com/archives/590
http://forensic-proof.com/archives/596
'Forensic > Theory' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Cluster Run 직접 확인해보기 - MFT엔트리찾기 (0) | 2015.12.31 |
|---|---|
| NTFS File System (6) MFT $SIA & $FN $DATA (0) | 2015.12.31 |
| NTFS File System (4) MFT (0) | 2015.12.29 |
| NTFS File System (3) VBR (0) | 2015.12.29 |
| NTFS File System (2) MBR & EBR (0) | 2015.12.29 |